Single-Area OSPF Concepts
OSPF overview
2.2.1 This page will introduce OSPF. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that is based on open standards. It is described in several standards of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The Open in OSPF means that it is open to the public and is non-proprietary.
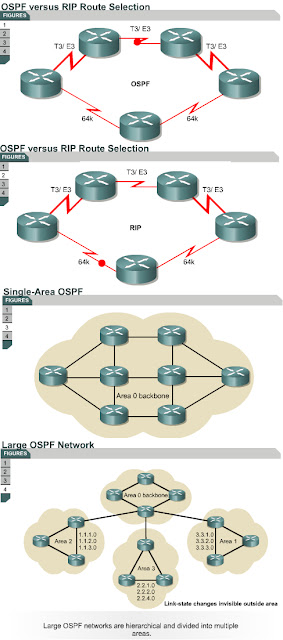
OSPF, when compared to RIP v1 and v2, is the preferred IGP because it is scalable. RIP is limited to 15 hops, it converges slowly, and it sometimes chooses slow routes because it ignores critical factors such as bandwidth in route determination. A drawback to using OSPF is that it only supports the TCP/IP protocol suite. OSPF has overcome these limitations and is a robust and scalable routing protocol that is suitable for modern networks. OSPF can be used and configured as a single area for small networks. It can also be used for large networks.
As shown in Figure , large OSPF networks use a hierarchical design. Multiple areas connect to a distribution area, or area 0 which is also called the backbone. The design approach allows for extensive control of routing updates. Area definition reduces routing overhead, speeds up convergence, confines network instability to an area, and improves performance.
The next page will provide more information about OSPF.
Certification-level claim: Configure routing protocols given user requirements.
Course-level claim: Describe, configure, verify, analyze, and troubleshoot the OSPF link-state routing protocol in a single area mode of operation.
Hands-on skills: none
This is a core TI.
This is an important overview of OSPF and links back to what the students already know about RIP. Ensure that the figures are discussed, especially Figures, which are animated when students press the white arrow. Remember to stress that OSPF uses areas to implement hierarchical routing as illustrated in Figure .
The following are points to emphasize when contrasting OSPF with RIP:
- OSPF only floods
changes to other routers instead of the entire routing table.
- OSPF supports
VLSM.
- OSPF overcomes
the hop count limit of RIP.
- OSPF is event
driven, whereas RIP broadcasts every 30 seconds.
- RIP sometimes
picks suboptimal paths, in terms of hops rather than bandwidth.
Comments
Post a Comment