Configuring RIP v2
1.2.4 This page will teach students how to configure RIP v2. RIP v2 is a dynamic routing protocol that is configured by naming the routing protocol RIP Version 2, and then assigning IP network numbers without specifying subnet values. This section describes the basic commands used to configure RIP v2 on a Cisco router.
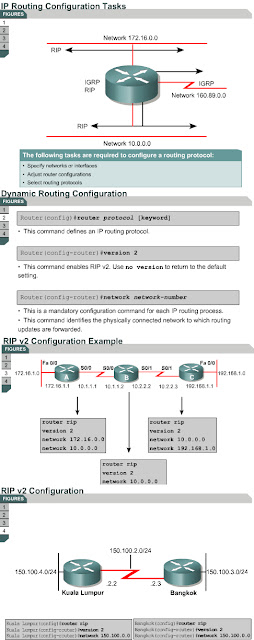
To enable a dynamic routing protocol, the following tasks must be completed:
The router command starts the routing process. The network command causes the implementation of the following three functions:
The router rip and version 2 commands combined specify RIP v2 as the routing protocol, while the network command identifies a participating attached network.
In this example, the configuration of Router A includes the following:
Figure shows another example of a RIP v2 configuration.
The Lab Activities on this page will show students how to convert RIP v1 to RIP v2.
The next page will describe the commands that are used to verify RIP v2
1.2.4 This page will teach students how to configure RIP v2. RIP v2 is a dynamic routing protocol that is configured by naming the routing protocol RIP Version 2, and then assigning IP network numbers without specifying subnet values. This section describes the basic commands used to configure RIP v2 on a Cisco router.
To enable a dynamic routing protocol, the following tasks must be completed:
- Select a routing
protocol, such as RIP v2.
- Assign the IP
network numbers without specifying the subnet values.
- Assign the
network or subnet addresses and the appropriate subnet mask to the
interfaces.
The router command starts the routing process. The network command causes the implementation of the following three functions:
- The routing
updates are multicast out an interface.
- The routing
updates are processed if they enter that same interface.
- The subnet that
is directly connected to that interface is advertised.
The router rip and version 2 commands combined specify RIP v2 as the routing protocol, while the network command identifies a participating attached network.
In this example, the configuration of Router A includes the following:
- router rip
– Enables RIP as the routing protocol
- version 2
– Identifies version 2 as the version of RIP being used
- network 172.16.0.0
– Specifies a directly connected network
- network 10.0.0.0
– Specifies a directly connected network
Figure shows another example of a RIP v2 configuration.
The Lab Activities on this page will show students how to convert RIP v1 to RIP v2.
The next page will describe the commands that are used to verify RIP v2


No comments:
Post a Comment