Destination unreachable message
8.1.8 This page will explain what a destination unreachable message is and why it occurs.
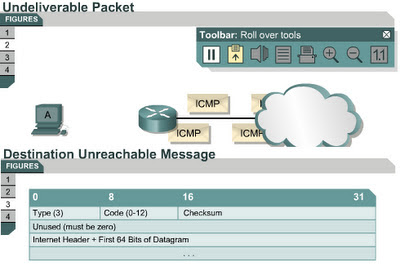
Datagrams cannot always be forwarded to their destinations. Hardware failures, improper protocol configuration, down interfaces, and incorrect routing information are some of the factors that prevent successful delivery. In these cases, ICMP sends the sender a destination unreachable message, which indicates that the datagram could not be forwarded.
Figure shows an ICMP destination unreachable message header. The value of 3 in the type field indicates it is a destination unreachable message. The code value indicates the reason the packet could not be delivered. Figure has a code value of 0, which indicates that the network was unreachable. Figure shows the meaning for each possible code value in a destination unreachable message.
A destination unreachable message may also be sent when packet fragmentation is required to forward a packet. Fragmentation is usually necessary when a datagram is forwarded from a Token Ring network to an Ethernet network. If the datagram does not allow fragmentation, the packet cannot be forwarded, so a destination unreachable message will be sent. Destination unreachable messages may also be generated if IP-related services such as FTP or Web services are unavailable. To effectively troubleshoot an IP network, it is necessary to understand the various causes of ICMP destination unreachable messages.
The next page introduces parameter problem messages.



No comments:
Post a Comment