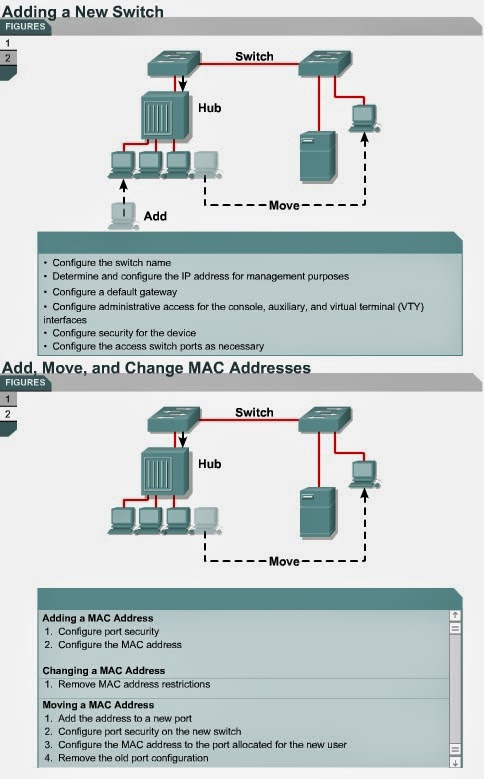
Spanning-Tree Protocol (Overview)
|
Redundancy in a network is critical. It allows networks to be
fault tolerant. Redundant topologies protect against network downtime, or
nonavailability. Downtime can be caused by the failure of a single link,
port, or network device. Network engineers are often required to balance the
cost of redundancy with the need for network availability. Redundant topologies based on switches and bridges are susceptible to broadcast storms, multiple frame transmissions, and MAC address database instability. These problems can make a network unusable. Therefore, redundancy should be carefully planned and monitored. Switched networks provide the benefits of smaller collision domains, microsegmentation, and full duplex operation. Switched networks provide better performance. Redundancy in a network is required to protect against loss of connectivity due to the failure of an individual component. However, this provision can result in physical topologies with loops. Physical layer loops can cause serious problems in switched networks. The Spanning-Tree Protocol is used in switched networks to create a loop free logical topology from a physical topology that has loops. Links, ports, and switches that are not part of the active loop free topology do not forward data frames. The Spanning-Tree Protocol is a powerful tool that gives network administrators the security of a redundant topology without the risk of problems caused by switching loops. This module covers some of the objectives for the CCNA 640-801 and ICND 640-811 exams. Students who complete this module should be able to perform the following tasks:
|